Electrical Preventative Maintenance
(EPM)
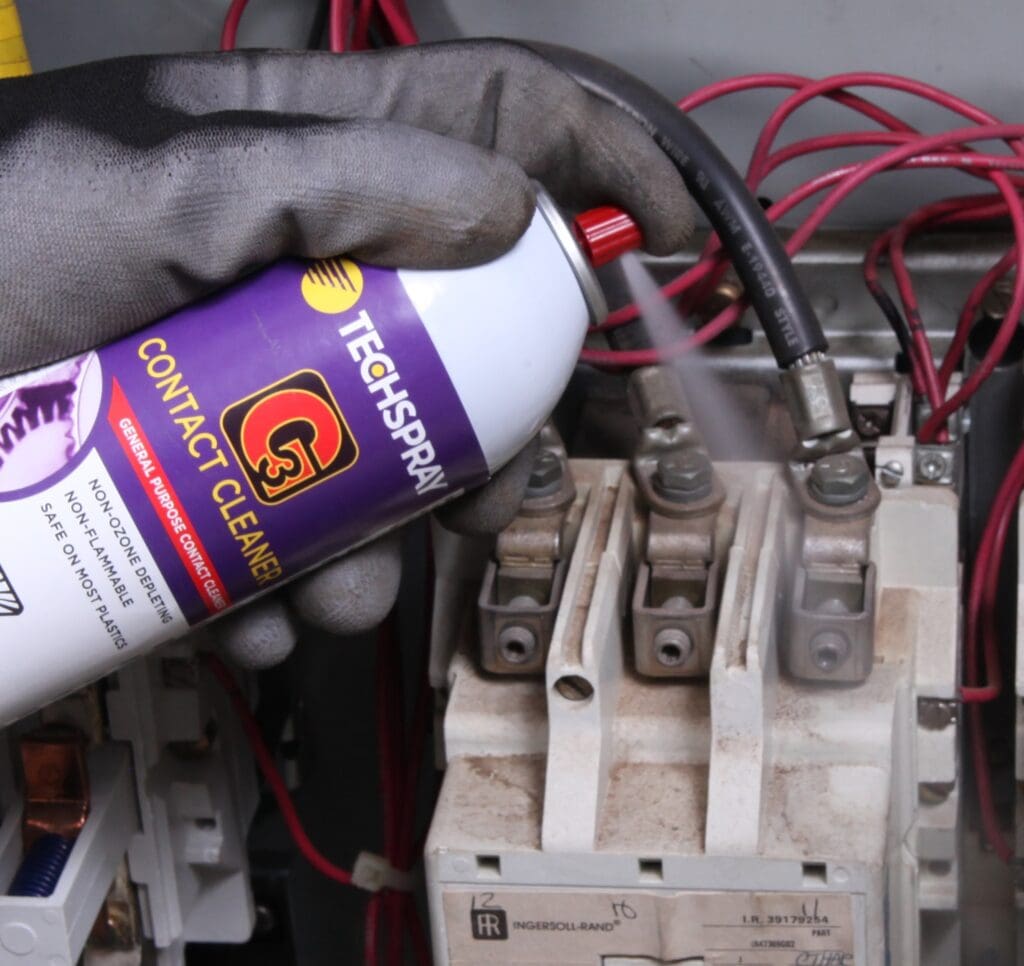
Poorly maintained electrical systems are a leading cause of business interruption, poor energy efficiency, and premature equipment breakdown. A well planned and executed electrical preventive maintenance (EPM) program will reduce equipment failures, unplanned downtime, and un-budgeted expenditures.
Attention Facility owners and Managers!!
ARE YOU COMPLIANT?
What were once electrical maintenance recommendations are now requirements!
ALERT! OSHA Can now utilize nfpa 70b standards to issue citations!
The US Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) looks to the prescriptive – based requirements of NFPA 70E & 70B to fulfill the performance – based requirements included in its standards.
CurrentSAFE® is your most reliable source to help you stay compliant with all recent changes in required nfpa standards.
CurrentSAFE® will Keep your facility protected
through our 3-step process.
STEP 1
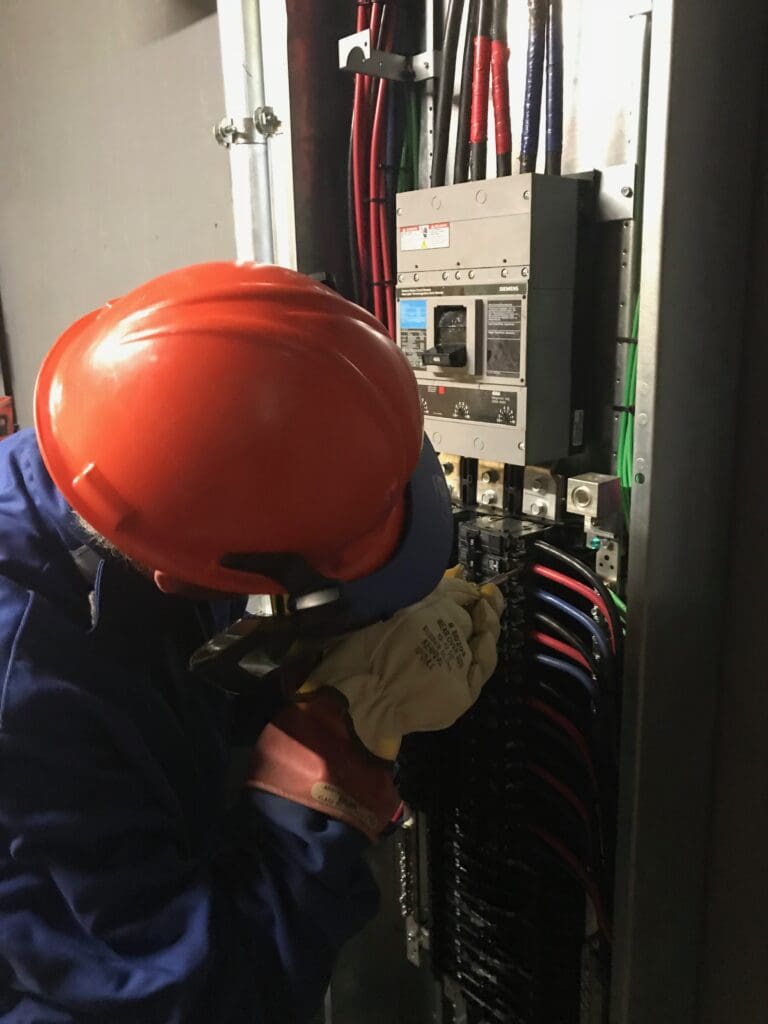
Our EPM Specialists tour your facility and identify critical electrical/power needs & determine what preventative maintenance services are needed to Keep You NFPA Compliant.
STEP 2
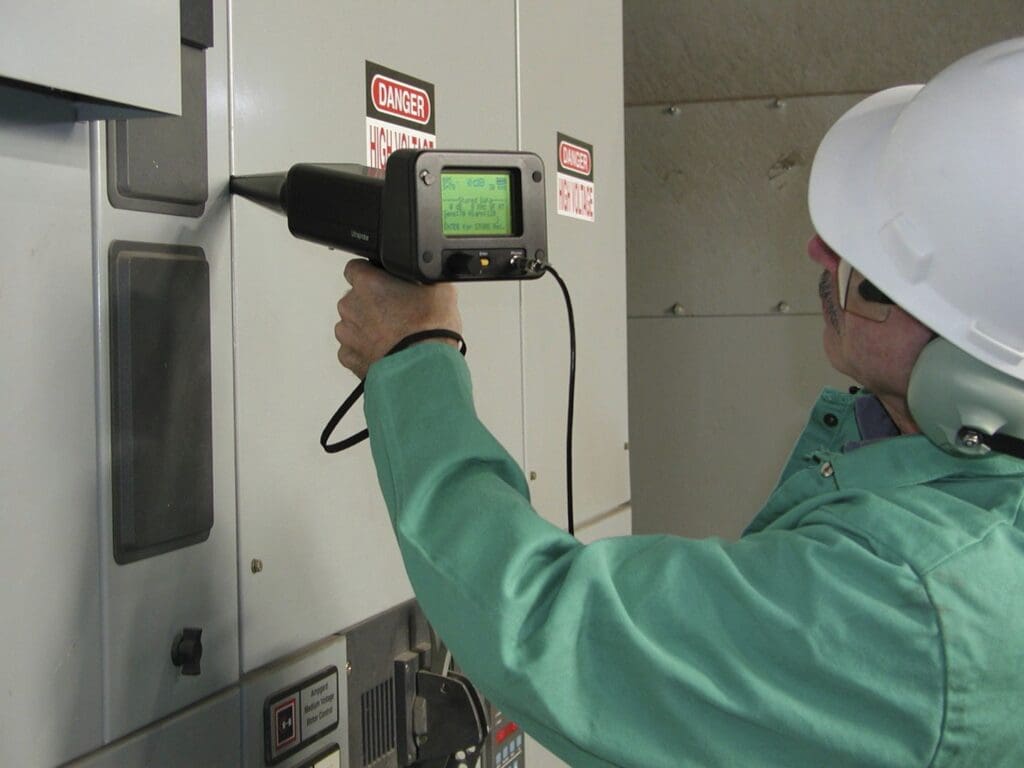
Our EPM Electricians will completely Test and Inspect your electrical distribution system including equipment and components.
STEP 3
A Customized Same Day Report of is completed and a plan is developed that helps your facility become and remain 70E & 70B Compliant.

The CurrentsAfe® EPM Advantage... Our exclusive epm480 advanced testing and reporting software
√ Same Day Reporting!
√ An Inventory List of Electrical Distribution Equipment and Components!
√ Digital Photo Documentation of Each Piece of Equipment!
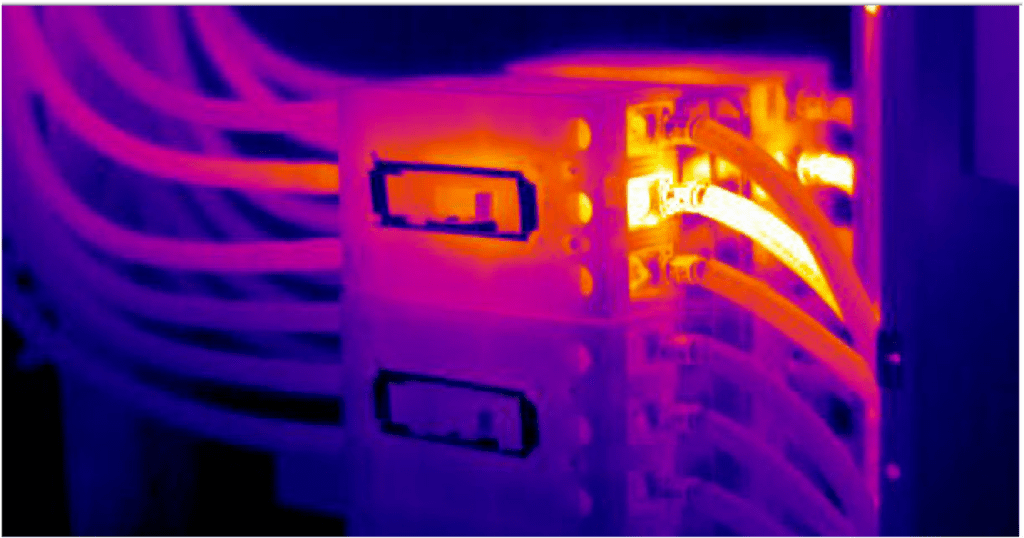
√ Infrared Images of Detected Hazards!
√ Descriptions and Recommended Actions of All Detected Hazards!

Menu of Services
About NFPA
NFPA was founded as—and still is—a self-funded nonprofit. But what started as a Boston-based organization for fire sprinkler codes has grown to become the leading global advocate for the elimination of death, injury, property, and economic loss due to fire, electrical, and related hazards.
The organization is combatting safety myths and misinformation by delivering expert knowledge through more than 300 codes and standards, innovate research, professional training, public education, and outreach and advocacy.
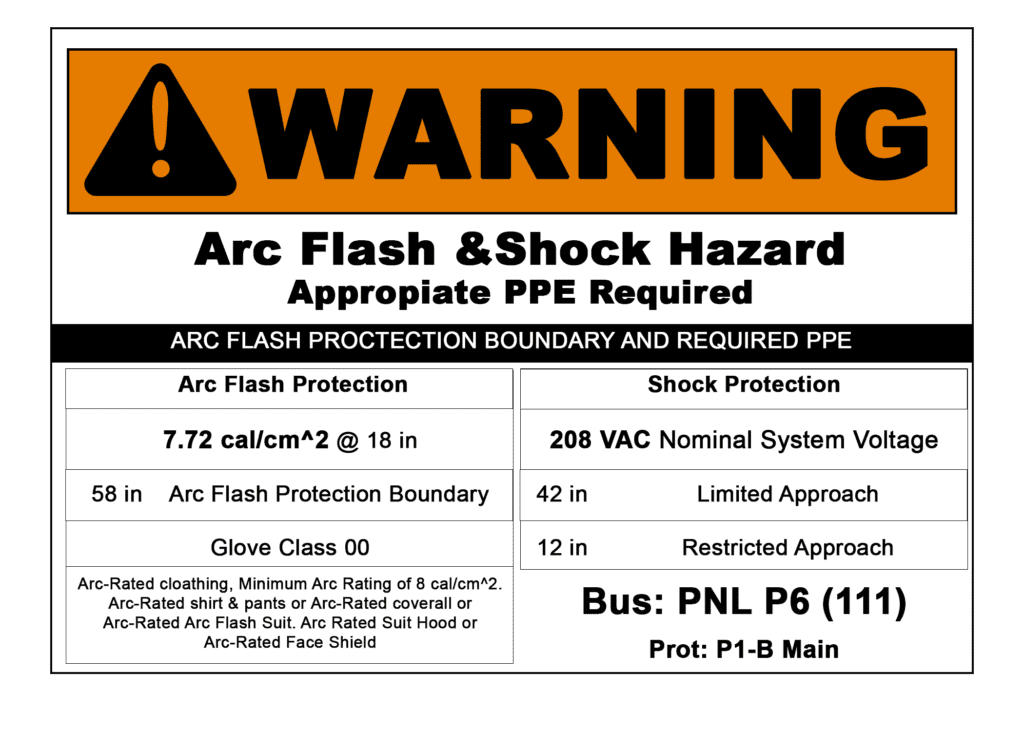
The NFPA’s 70E & 70B books of standards set forth the REQUIREMENTS to protect personnel from by reducing exposure to arc flash, arc blast, and electrical hazards.

NFPA 70E
The National Fire Protection Association’s NFPA 70E is an internationally accepted American National Standard that defines electrical safety-related work practices.
6 Keys to Compliance
Owners MUST maintain electrical equipment in accordance with manufacturers’ instructions or industry consensus standards to reduce the risk associated with failure. Here are the six keys to compliance:
- Perform maintenance on all electrical equipment.
- Perform a hazard/risk assessment & label equipment.
- Generate andpost a facility one-line drawing.
- Understand NFPA 70E/have a complete 70E safety plan.
- Train and qualify employees in NFPA 70E compliance.
- Provide appropriate personal protective equipment.
NFPA 70B
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 70E details preventive maintenance for electrical, electronic, and communication systems and equipment in industrial commercial and institutional facilities to prevent equipment failures and worker injuries.
Required Electrical Maintenance Plan
Section N 4.2.4.2 of the NFPA 70B Book Standards sates…..
“All Commercial, Industrial, and Institutional Facilities MUST Create and Keep an Electrical Maintenance Plan (EMP) that Will Include the Following Elements…”
REQUIREMENT 1: Create an electrical safety program that addresses the condition of maintenance;
REQUIREMENT 2: Identify responsible personnel for implementing each element of the program;
REQUIREMENT 3: Survey and analyze of electrical equipment and systems to determine maintenance requirements and priorities;
REQUIREMENT 4: Develop and document maintenance procedures for equipment;
REQUIREMENT 5: Create a plan of inspections, servicing, and suitable tests;
REQUIREMENT 6: Develop a maintenance, equipment, and personnel documentation and records-retention policy;
REQUIREMENT 7: Develop a process to prescribe, implement, and document corrective measures based on collected data;
REQUIREMENT 8: A process for incorporating design for maintainability in electrical installations;
REQUIREMENT 9: A program review and revision process that considers failures and findings for continuous improvement.
4 of the Top 10 OSHA Violations are Electrical Related
Every year, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) announces the most frequently cited workplace violations for the year. Here are 4 of the the top 10 violations spanning the 2018 fiscal year (Oct. 1, 2017–Sept. 30, 2018).
The list below represents the electrical related violations from the OSHA top 10 violations
- Lockout/tag-out (29 CFR 1910.147) The lockout/tag-out regulation protects employees from unexpected machine startups or hazardous releases during servicing and maintenance. Failing to lockout equipment, have a written program and conduct annual inspections of machine-specific procedures are the most common violations.
- Personal protective equipment (29 CFR 1910.132) OSHA requires all employers to conduct a formal written workplace hazard assessment to determine what personal protective equipment is required to protect employees from injuries. In addition, employers are required to provide the personal protective equipment and provide employee training on its proper use. Failure to conduct the assessment and certify it is a commonly overlooked requirement.
- Electrical safety (29 CFR 1910.305) This is one of several OSHA regulations addressing electrical safety and includes access to breaker boxes, breaker identification and guarding. Common violations under this standard involve blocked access to breaker boxes, open breakers, missing knockouts in junction or breaker boxes, and no or incomplete labeling of breakers.
- Electrical safety (29 CFR 1910.303) This regulation addresses methods, components and equipment. Common violations under this standard involve the use of extension cords, power strips, improper pendant drops and frayed wiring.